Learning how to design an energy efficient building is a key part of creating a sustainable future. It’s essential to think about how we can reduce our carbon footprint and lower the amount of energy consumed by buildings. With careful planning, it’s possible to design an energy-efficient building that not only reduces environmental impact but also cuts down on operational costs.
By considering factors such as heating and cooling systems, lighting solutions, water conservation strategies, and renewable energy options, you can create a structure with maximum efficiency while minimizing its environmental impact.
Let’s get started with how to design an energy efficient building that benefits generations to come.
Table of Contents
How to Design an Energy Efficient Building
The building design is an important factor in creating an energy-efficient building. More importantly, building materials play a crucial role in how much energy a building will consume.
Building materials can have a big impact on the overall efficiency of a structure. Using materials with high thermal mass such as brick or concrete can help to regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night.
Properly insulating walls, ceilings, floors, and other areas of the building envelope is essential for reducing energy consumption. Insulation helps keep warm air inside during winter months and cool air inside during summer months, which reduces heating/cooling costs significantly.
There are many types of insulation available including fiberglass batts, spray foam, cellulose loose-fill insulation, and rigid foam boards so it’s important to research each option carefully before choosing the type of insulation for your building project.
Heating and Cooling Systems
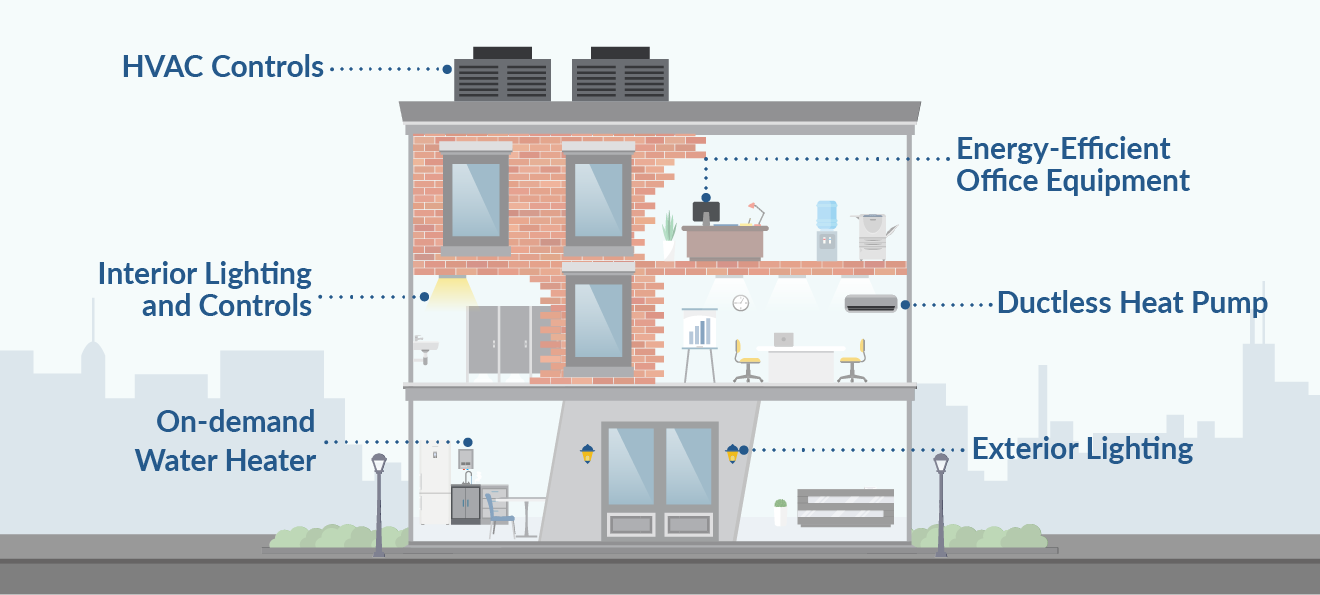
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems are also crucial components of how to design an energy-efficient building.
How to Select an HVAC System
Size, location, and climate should be taken into consideration when selecting an HVAC system. For example, if a building is located in a hot and humid climate, then an air conditioner with higher SEER ratings would be necessary to keep the interior comfortable.
It’s also important to consider how many people will occupy the space since this affects the size of the unit needed.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating measures how efficient an air conditioning unit is at cooling down a room. A higher SEER rating means that more energy can be saved when cooling down the same amount of space compared to units with lower SEER ratings.
Look for models with high SEER ratings when selecting an HVAC system for maximum energy savings.
Zoning Requirements
Zoning considerations are also important when selecting an HVAC system because different areas require different types of systems. For instance, some buildings may need multiple zones so that certain areas can have separate temperature controls while areas with low occupancy don’t need them at all.
By zoning correctly, you do not have to run heating/cooling systems in unoccupied spaces during off-peak hours which helps reduce overall energy consumption.
Next, we’ll look at lighting solutions to further reduce energy consumption in our building design.
 (Source)
(Source)
Lighting Solutions
LED lights are one of the most energy-efficient lighting solutions available. They use up to 90% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last up to 25 times longer. LEDs also produce very little heat, making them a great choice for both indoor and outdoor applications.
LED lights can be used in a variety of ways, from spotlights to task lighting, and they come in many different colors and styles.
Natural light sources such as skylights can provide an abundance of natural light into any space without using electricity. By strategically placing windows throughout your building, you can reduce the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours while still providing plenty of natural light inside.
Additionally, adding window treatments like blinds or curtains will help control how much sunlight enters your space at certain times.
Next, we will discuss water conservation strategies that can be implemented in the design of an energy-efficient building.
Water Conservation Strategies
Installing low-flow fixtures such as toilets, showerheads, and faucets can save up to 20 gallons of water per day per person.
Additionally, installing energy-efficient dishwashers and washing machines can also help conserve water by using less hot water during operation.
Rainwater collection systems capture rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces for use in irrigation or other purposes within the building. These systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to reduce strain on municipal water supplies while providing a free source of clean water for occupants. Rainwater collection systems typically include gutters that direct runoff into tanks where it is stored until needed.
Greywater reuse systems collect wastewater from showers, sinks, and laundry machines for reuse in toilet flushing or irrigation applications. This type of system helps reduce strain on municipal sewer systems while providing an additional source of usable greywater that would otherwise be wasted down the drain.
Proper planning and installation are necessary to ensure these systems meet local codes and regulations regarding wastewater treatment standards before being put into service.
Renewable Energy Options
Solar panels are one of the most popular renewable energy options available for commercial buildings. Solar panels use photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be used to power lights, appliances, and other electrical devices in a building.
Solar panels require minimal maintenance and can provide significant savings on utility bills over time. Plus, they are easy to install and come in a variety of sizes and styles that can fit any budget or aesthetic preference.
Wind turbines are another renewable energy option that is becoming increasingly popular among building designers. Wind turbines generate electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy from the wind passing through their blades. This type of system requires more space than solar panels but may offer greater cost savings depending on local wind conditions.
Additionally, many states offer tax credits for installing wind turbines as an incentive for people to switch to this form of renewable energy.
FAQs About How to Design an Energy Efficient Building
What shape of building is the most energy-efficient?
The most energy-efficient building shape is a cube or box. This shape has the least surface area for its volume, which means it requires less energy to heat and cool than other shapes.
Additionally, cubes are easier to insulate due to their uniform walls and corners. The lack of protrusions also reduces air infiltration, further improving efficiency.
Finally, cubes can be easily stacked on top of each other in multi-story buildings without wasting space between them. This makes them ideal for urban areas where space is limited.
What is the most efficient building design?
When it comes to energy efficiency, dome-shaped homes top the list. These homes have fewer corners and are thus more aerodynamic. Wind can easily travel over these houses, reducing pressure changes and minimizing energy loss.
What are three materials that are used to improve the energy efficiency of a building?
Organic materials such as rammed earth, wood, and straw are an alternative to conventional building materials such as cement and steel. While natural and environmentally friendly, these organic materials are incredibly durable and provide superior thermal insulation.
What is the most energy-efficient building material?
- Insulating Concrete Forms.
- PIR Foam Energy Bricks.
- Straw and Stucco.
- Compressed Soil.
- Structural Insulated Panels.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels.
- Plant-Based Polyurethane Insulation.
- Low-Emissive Windows.
Conclusion
An energy-efficient building has energy-efficient heating, cooling, and lighting systems, water conservation strategies, and renewable energy sources. With careful planning and consideration of all these elements, you can make sure your investment pays off for years to come.
We need to take action now! By utilizing the latest technologies in how to design an energy efficient building, we can reduce our environmental footprint while also cutting down on costs associated with energy consumption. Through a collaborative effort between architects, engineers, and developers, it is possible to create structures that are both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Let’s work together towards creating an eco-friendly future for ourselves!
{“@context”:”https:\/\/schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What shape of building is the most energy-efficient?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
The most energy-efficient building shape is a cube or box. This shape has the least surface area for its volume, which means it requires less energy to heat and cool than other shapes.
Additionally, cubes are easier to insulate due to their uniform walls and corners.\u00a0The lack of protrusions also reduces air infiltration, further improving efficiency.
Finally, cubes can be easily stacked on top of each other in multi-story buildings without wasting space between them. This makes them ideal for urban areas where space is limited. “}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is the most efficient building design?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
When it comes to energy efficiency, dome-shaped homes top the list.\u00a0 These homes have fewer corners and are thus more aerodynamic. Wind can easily travel over these houses, reducing pressure changes and minimizing energy loss. “}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What are three materials that are used to improve the energy efficiency of a building?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Organic materials such as rammed earth, wood, and straw are an alternative to conventional building materials such as cement and steel. While natural and environmentally friendly, these organic materials are incredibly durable and provide superior thermal insulation. “}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is the most energy-efficient building material?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
- \n\t
- Insulating Concrete Forms.\n\t
- PIR Foam Energy Bricks.\n\t
- Straw and Stucco.\n\t
- Compressed Soil.\n\t
- Structural Insulated Panels.\n\t
- Vacuum Insulation Panels.\n\t
- Plant-Based Polyurethane Insulation.\n\t
- Low-Emissive Windows.\n
- Insulating Concrete Forms.
- PIR Foam Energy Bricks.
- Straw and Stucco.
- Compressed Soil.
- Structural Insulated Panels.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels.
- Plant-Based Polyurethane Insulation.
- Low-Emissive Windows. “}}]}





