Making your buildings more energy-efficient can be a boon when it comes to saving money on utility bills and reducing your carbon footprint. Whether you’re looking to upgrade an existing building or construct an entirely new structure, there are several strategies that can help improve your overall efficiency rating. But first, what is a good building efficiency ratio?
The building efficiency ratio refers to how efficiently a building consumes energy and resources. It takes into account factors such as insulation, lighting, HVAC systems, water conservation, and sustainable construction materials. A good building efficiency ratio can lead to lower energy costs and improved environmental performance.
Let’s break down what is a good building efficiency ratio so you can achieve a higher level of efficiency for your property.
Table of Contents
What is a Good Building Efficiency Ratio?
Before we determine what is a good building efficiency ratio, let us first define what is a building efficiency ratio and why it is an important metric for your business operations.
The building efficiency ratio (BER) is calculated by dividing the total amount of energy consumed over a given period (usually one year) by the total potential available energy during that same period. This calculation gives an indication of how much energy could have been saved if more efficient methods had been employed throughout the design and construction process.
Benefits of a Good Building Efficiency Ratio
A good BER indicates that your building has been designed with maximum efficiency in mind, meaning you will save money on your utility bills while also reducing your carbon footprint.
Calculating the Building Efficiency Ratio
To calculate your BER, you will need accurate records detailing all forms of energy usage within your property over 12 consecutive months including both natural (e.g sunlight) and artificial (e.g central heating) resources.
Divide this figure by the total potential available energy over that same time frame. You can find this information on completion or inspection reports.
Once these figures have been obtained, simply divide them together giving you an overall percentage rating out of 100%. Anything above 50% would indicate good performance whereas anything below 40% would suggest there may be room for improvement when it comes to increasing efficiencies within your property.
A good building efficiency ratio can help to reduce energy costs, improve occupant comfort and health, and increase the value of a property. By utilizing energy-efficient design strategies, you can further improve your building efficiency ratio.
Energy-Efficient Design Strategies
There are plenty of ways you can increase your building efficiency ratio.
Insulation
Insulation and air sealing techniques can help reduce heat loss or gain, which is one of the most important steps in improving energy efficiency. By using insulation materials such as foam board, spray foam, fiberglass batts, and cellulose to seal gaps around windows and doors, you can prevent unwanted air infiltration into your building.
Installing weather stripping around door frames can also help keep conditioned air inside the building while preventing outside air from entering.
Lighting
Lighting is another key factor when it comes to energy efficiency. Selecting efficient lighting fixtures such as LED bulbs that use less electricity than traditional incandescent bulbs will not only save money on utility bills but also improve the overall quality of light in the workplace.
Installing motion sensors can further reduce energy consumption by automatically turning off lights when they’re not needed.
HVAC
High-efficiency HVAC systems are an important part of any energy-efficient design strategy because they provide consistent temperatures throughout a building while using less electricity.
In addition to selecting an efficient system with high SEER ratings, proper maintenance should be performed regularly to ensure optimal performance of your HVAC system.
Finally, utilizing daylight harvesting technology allows natural sunlight to be used during daytime hours which is a great way to take advantage of free renewable resources.
Energy-efficient design strategies are key to achieving a good building efficiency ratio. With the right insulation, lighting, and HVAC systems, you can reduce energy consumption significantly.
Now let’s move on to water conservation strategies for improving your building efficiency ratio.
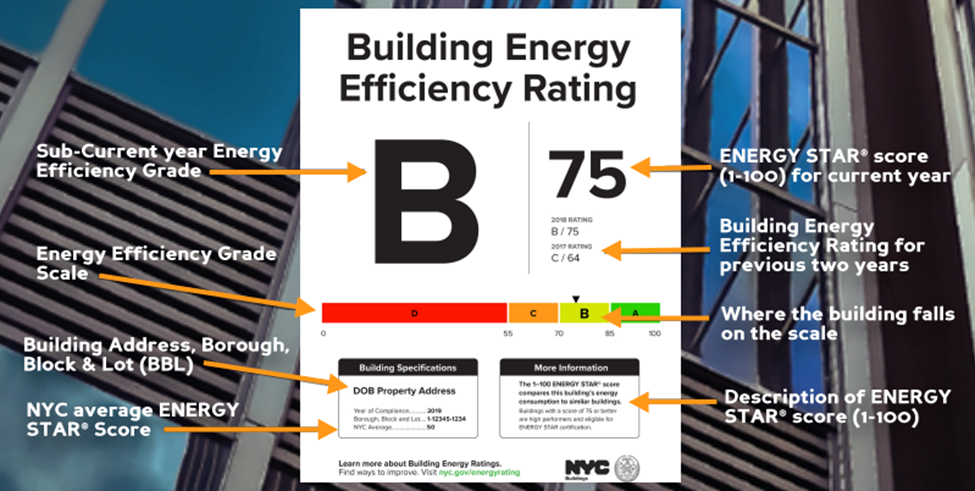 (Source)
(Source)
Water Conservation Strategies
Water conservation is essential to achieving what is a good building efficiency ratio. Low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and greywater reuse are all effective methods of conserving water in buildings.
Low-Flow Fixtures
Low-flow fixtures such as toilets, showerheads, and faucets can help reduce the amount of water used in a building by up to 50%. These fixtures use less water per flush or cycle than traditional models while still providing adequate performance. Installing low-flow fixtures is an easy way to reduce the amount of water consumed without sacrificing comfort or convenience for your tenants.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting rain from rooftops or other surfaces and storing it for later use. This stored rainwater can then be used for irrigation purposes or other non-potable applications such as flushing toilets or washing parking lots. By using harvested rainwater instead of potable (drinking) water, buildings can significantly reduce the strain on the municipal water supply while also saving money on operating expenses.
Greywater Reuse
Greywater is wastewater generated from sinks, showers, bathtubs, laundry machines, and other household activities that do not contain human waste like urine or feces. This type of wastewater can be reused for landscape irrigation or toilet flushing if treated specifically for this purpose. By reusing greywater instead of relying solely on potable sources for these tasks, buildings can save both energy and money while also helping conserve valuable drinking water supplies.
Sustainable Materials and Construction Practices
Sustainable materials are those that are made from recycled content or sourced locally to reduce transportation impacts on the environment.
Recycled content materials can include items such as insulation, drywall, and roofing shingles. These products have been created using post-consumer waste, reducing the amount of new material required for construction projects.
Local sourcing of building materials is also beneficial for sustainability because it reduces the environmental impact associated with long-distance shipping and transport. This includes sourcing lumber from local sawmills or purchasing stone pavers from a nearby quarry instead of importing them from another region or country.
Waste reduction strategies during construction activities can help improve a building’s overall efficiency ratio by minimizing resource consumption and preventing unnecessary waste generation.
Reusing existing materials whenever possible is one way to reduce waste while still achieving desired results in terms of aesthetics and performance. For example, salvaged wood flooring may be used instead of installing new hardwood floors. This not only eliminates the need for additional resources but also adds character to the space through its unique appearance.
Additionally, demolition debris can often be reused as filling material in landscaping projects around the property rather than being sent offsite to landfills or incinerators.
Conclusion
A good building efficiency ratio is achievable with the right design strategies, water conservation measures, and sustainable materials and construction practices. By investing in these areas of improvement now, you can ensure that your building will remain energy-efficient for years to come.
With the right plan in place and proper implementation of these strategies, you can achieve what is a good building efficiency ratio to benefit both your bottom line and the environment. Let’s take action today!





