How do you make the most out of your space and resources? By knowing how to calculate building efficiency, you can identify areas that need improvement as well as potential strategies for increasing energy efficiency.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how to calculate building efficiency, discuss different approaches to increasing energy savings and cost-effectiveness, review financing options for efficiency renovations, and outline a plan of action that will ensure maximum return on your investments.
Table of Contents
What is Building Efficiency?
Building efficiency is the measure of how well a building uses energy to provide its occupants with comfortable working conditions. It takes into account factors such as insulation, lighting, heating, cooling, ventilation, renewable energy sources, and other elements that affect how much energy is consumed in a given space.
Improving building efficiency can have significant benefits for both the environment and for reducing operational costs.
Factors Affecting Building Efficiency
There are many different factors that can influence building efficiency, including insulation levels in walls and ceilings, airtightness of windows and doors, type of HVAC system used (e.g., forced-air vs radiant heat), quality of lighting fixtures installed (LEDs versus incandescent bulbs), presence/absence of renewable energy sources, availability/usefulness of weatherization measures, and water conservation efforts.
All these components work together to determine how much power needs to be expended in order for a structure’s interior temperature to remain comfortable year-round while also reducing the environmental impact of wasted resources and gas emissions.
Benefits of Improving Building Efficiency
Improving building efficiency has numerous advantages beyond just saving money on utility bills. It can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with burning fossil fuels, which contribute significantly towards climate change worldwide.
More efficient buildings also require less maintenance, thanks to energy-efficient construction materials. This translates into fewer repair costs since there will be less wear and tear on your building.
Finally, improved indoor air quality resulting from tighter seals around windows and doors combined with better ventilation systems leads to healthier environments where occupants are less vulnerable to respiratory illnesses caused by poor air circulation in the workplace.
How to Calculate Building Efficiency
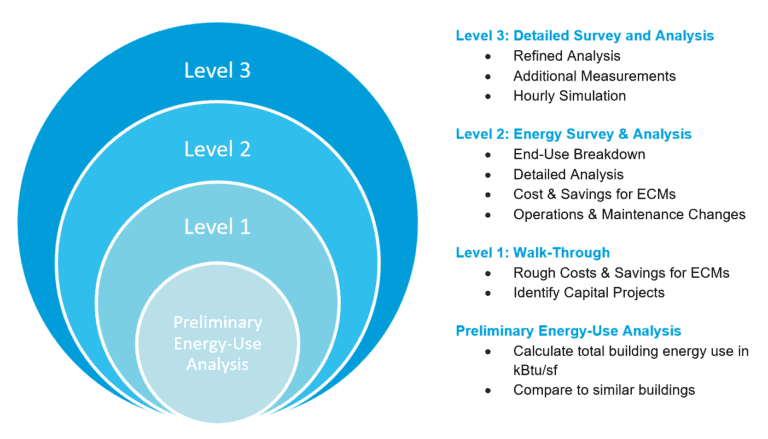
The first step in how to calculate building efficiency is establishing a baseline measurement of how much energy your building currently consumes. This can be done by conducting an energy audit or comparing data from previous utility bills. Knowing the current level of usage will help identify potential areas for improvement and track progress once changes have been implemented.
Once you have established your baseline energy use, you can begin looking at specific areas where improvements could be made. Common areas include lighting systems, HVAC systems, insulation levels, weatherization techniques such as caulking around windows and doors, and incorporating renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines into your building design. All these elements should be evaluated in order to determine which ones need attention first.
After implementing changes designed to increase building efficiency, it is important to measure their effectiveness by tracking utility bills or conducting regular audits that compare current usage with previous baseline measurements. By doing so, you can accurately gauge whether or not your efforts are paying off and make adjustments if necessary.
(Source)
Strategies for Improving Building Efficiency
Lighting and HVAC Systems
One of the most effective strategies for improving building efficiency is to upgrade lighting and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Replacing outdated or inefficient fixtures with LED bulbs can reduce energy consumption by up to 80%.
Additionally, installing programmable thermostats can help regulate temperatures in a space more efficiently. Installing motion sensors on lights can also save energy by automatically turning them off when not in use.
Insulation and Weatherization
Another important strategy for increasing building efficiency is insulation and weatherization. Insulating walls, ceilings, windows, doors, pipes, ducts, floors — basically any area that separates heated or cooled air from the outside air — can help keep conditioned air inside the building while preventing outdoor elements from entering it.
Sealing cracks around windows and doors will also prevent drafts from coming into the space. In addition to helping maintain comfortable temperatures indoors all year round, proper insulation helps lower energy bills as well.
Renewable Energy Sources
Finally, incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines into a building’s design can drastically improve its overall efficiency levels. Solar power provides clean electricity from the sun while wind turbines harness the power of kinetic energy produced by moving air currents outdoors. Both options are cost-effective ways to reduce dependence on nonrenewable resources while still providing reliable power sources for buildings in the long term.
Financing Options for Increasing Building Efficiency
Tax credits and incentives are a great way to finance energy efficiency improvements for buildings. Tax credits can be used to reduce the amount of taxes owed, while incentives may provide direct payments or reimbursements for certain projects.
For example, the federal government offers tax credits for businesses that install solar panels or other renewable energy sources on their property. Some states also offer additional incentives such as rebates and grants which can help offset the cost of installing these systems.
Grants are typically provided by government agencies at either the state or federal level in order to encourage investment in energy-efficient technologies. These grants can cover a wide range of activities from purchasing new equipment to staff training.
Rebates may also be offered by utility companies when customers purchase specific types of energy-efficient products such as lighting fixtures or HVAC systems with high Energy Star ratings.
Low-interest loans are an attractive financing option for many building owners who want to make upgrades but don’t have enough cash upfront. These loans allow borrowers to access funds with lower interest rates than traditional bank loans, making them more affordable in the long run if you plan ahead and budget accordingly. It is important to ensure that you will be able to comfortably make reasonable monthly payments without causing financial stress when payment is due.
Conclusion
Improving the energy efficiency of your buildings can help you save money, reduce your environmental impact, and create a more comfortable space for your tenants or employees. By understanding how to calculate building efficiency, exploring strategies for improvement, and implementing an effective plan of action, you can make sure that your efforts are successful in increasing the overall efficiency of your building.
We need to take action now to reduce energy costs, improve air quality and protect the environment. By implementing an effective system of monitoring and measuring a building’s performance, we can identify areas for improvement that will lead us toward greater sustainability. Together, let’s create efficient buildings that benefit everyone!





