Have you ever wondered what deregulation is and why it happens? Here’s the deregulated definition: deregulation occurs when the government removes regulations from an industry. This can have both positive and negative impacts on businesses and consumers.
Let’s take a closer look at the deregulated definition, how it affects different groups and some of the pros and cons associated with this process.
Table of Contents
- Deregulated Definition
- The History of Deregulation in the United States
- Deregulation and Its Impact on Consumers
- Deregulation and Its Impact on Businesses
- Deregulation in the Energy Sector
- The Pros and Cons of Deregulation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the meaning of deregulation?
- What is an example of deregulation?
- What is another word for deregulation?
- Is deregulation good or bad for the economy?
- Conclusion
Deregulated Definition
Deregulation occurs when the government decreases its regulation of a particular industry. This can happen through laws or regulations that are passed by the government, or through a government agency changing its policies.
When an industry is deregulated, it means that there are fewer rules and regulations governing how the industry operates. This can lead to more competition within the industry, and it can also lead to lower prices for consumers.
The History of Deregulation in the United States
The deregulation of the United States began in the 1970s and was a response to the increasing cost of living and doing business in the country. The goal of deregulation was to lower prices and encourage competition.
The results were mixed, and the process was often messy and complicated. The first industry to be deregulated was the trucking industry.
This led to a decrease in the cost of shipping goods and an increase in the efficiency of the industry. However, it also led to a decrease in the quality of service, as trucking companies began to cut corners to save money.
The next industry to be deregulated was the airline industry. This had a similar effect on the trucking industry, with prices falling and quality declining.
The most notable change was the introduction of “hub-and-spoke” routing, which resulted in longer flight times and more connections.
The third and most controversial industry to be deregulated was the telecommunications industry.
The goal of deregulation here was to increase competition and lower prices. However, the result was a decrease in the quality of service and an increase in the cost of living for consumers.
The fourth and final industry to be deregulated was the electricity industry. The goal here was to encourage competition and lower prices.
However, the result was an increase in electricity rates and lower quality of service.
Overall, the results of deregulation have been mixed.
Prices have fallen in some industries, but the quality has often declined as well.
Deregulation and Its Impact on Consumers
Deregulated definition refers to the elimination or reduction of government regulations on businesses and industries. This can have a number of impacts on consumers, both positive and negative.
On the positive side, deregulation can lead to more competition and lower prices for consumers. It can also encourage innovation and new businesses.
On the negative side, deregulation can lead to higher prices and fewer choices for consumers. It can also lead to environmental damage and other negative consequences.
Overall, deregulation can be a good or bad thing for consumers depending on the specific situation.
Deregulation and Its Impact on Businesses
For businesses, deregulation definition means the removal of government regulations in order to create a more free market. The impact of deregulation can be both positive and negative, depending on the industry.
For example, the airline industry has been largely deregulated since 1978. This has led to increased competition and lower prices for consumers.
However, it has also led to fewer options for routes and airlines, and less job security for employees.
The banking industry was also deregulated in the 1990s. This led to the formation of large banks that were “too big to fail.”
When the housing market collapsed in 2008, these banks received billions of dollars in bailouts from the government.
This led to public outrage and more regulations being placed on the banking industry.
Some industries, such as airlines and banking, have been largely deregulated with mixed results. Other industries, such as healthcare and energy, are still heavily regulated.
The debate over deregulation will continue as new industries emerge and old industries change.
 (Source)
(Source)
Deregulation in the Energy Sector
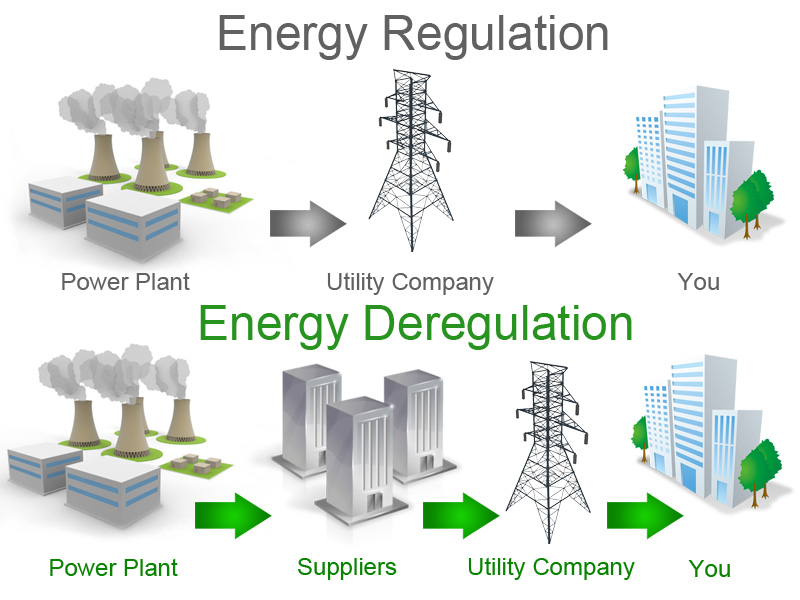
In certain parts of North America, electricity prices are regulated by a governmental or governing body. The utility companies themselves are the only entities allowed to sell to consumers.
Utility companies set the price of electricity and gas, along with the cost of transporting and distributing these utilities. Therefore, consumers cannot choose their electricity or energy providers.
Many states across North America have deregulated their electricity market, allowing competitive energy suppliers to enter the market and supply power to consumers.
In these areas, energy is not regulated by the government. Instead, the prices are set by the energy companies themselves. Consumers can shop around and choose their provider, much like they do with cable or internet providers.
With deregulation, the power is in your hands. You can choose your natural gas or electricity provider, and this competition between providers means that they’re forced to innovate and offer new products and services.
In deregulated energy, green energy supports the production and use of renewable resources in the generation of power, making the overall process more environmentally friendly.
In a deregulated gas industry, these green energy options help to support projects that reduce emissions of harmful greenhouse gases.
With more competitors entering the market, you can benefit from a wider variety of products, which guarantees that up to 100 percent of the electricity you use is offset with renewable energy.
Your local distribution/utility companies will still continue to deliver your energy supply, even though you will be getting it from a different source.
The Pros and Cons of Deregulation
The goal of deregulation is to lift government restrictions to create a more competitive marketplace that will benefit consumers through lower prices and better products and services.
There are both pros and cons to deregulation. On the plus side, it can lead to more competition and choice for consumers. It can also encourage businesses to be more innovative and efficient.
On the downside, deregulation can lead to higher prices for some goods and services, and it can also create instability in markets.
When it comes to deregulation, the key is to strike a balance that will create the most benefits for consumers and businesses alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the meaning of deregulation?
The definition of deregulation is when a government removes restrictions on industry, allowing companies to compete freely in the marketplace.
What is an example of deregulation?
The deregulation of the airline industry is an example of deregulation.
What is another word for deregulation?
Deregulation can mean different things depending on the context, but some common definitions are liberalization and privatization.
Is deregulation good or bad for the economy?
There is no simple answer to this question as it depends on a number of factors. Generally, deregulation can lead to more competition and choice in the marketplace, which can be good for consumers and businesses.
However, it can also lead to higher prices and less stability in certain markets.
Conclusion
Deregulation can be a complex and controversial topic. But at its core, deregulated definition simply refers to the removal of government regulations from an industry.
This process can have different impacts on businesses and consumers, depending on the industry involved. While there are some potential benefits associated with deregulation, it’s important to weigh these against the possible risks before making any decisions.





